In the vast realm of the manufacturing industry, plastic molds are like crucial gears that drive the production of numerous plastic products. When cooperating with mold factories, one of the most concerning issues for many clients is how long the manufacturing cycle of plastic molds will be. After all, this directly affects the time-to-market and production progress of products. However, the manufacturing of plastic molds is far from a simple assembly-line operation. It is an extremely complex and delicate process that cannot be completed in a short period. There are numerous and intricate factors influencing their delivery time, and mold factories must conduct comprehensive project management and control to ensure on-time delivery. So, what exactly are the factors that determine the delivery time of plastic molds?
Client Feedback: The “Conducting Baton” Determining Progress
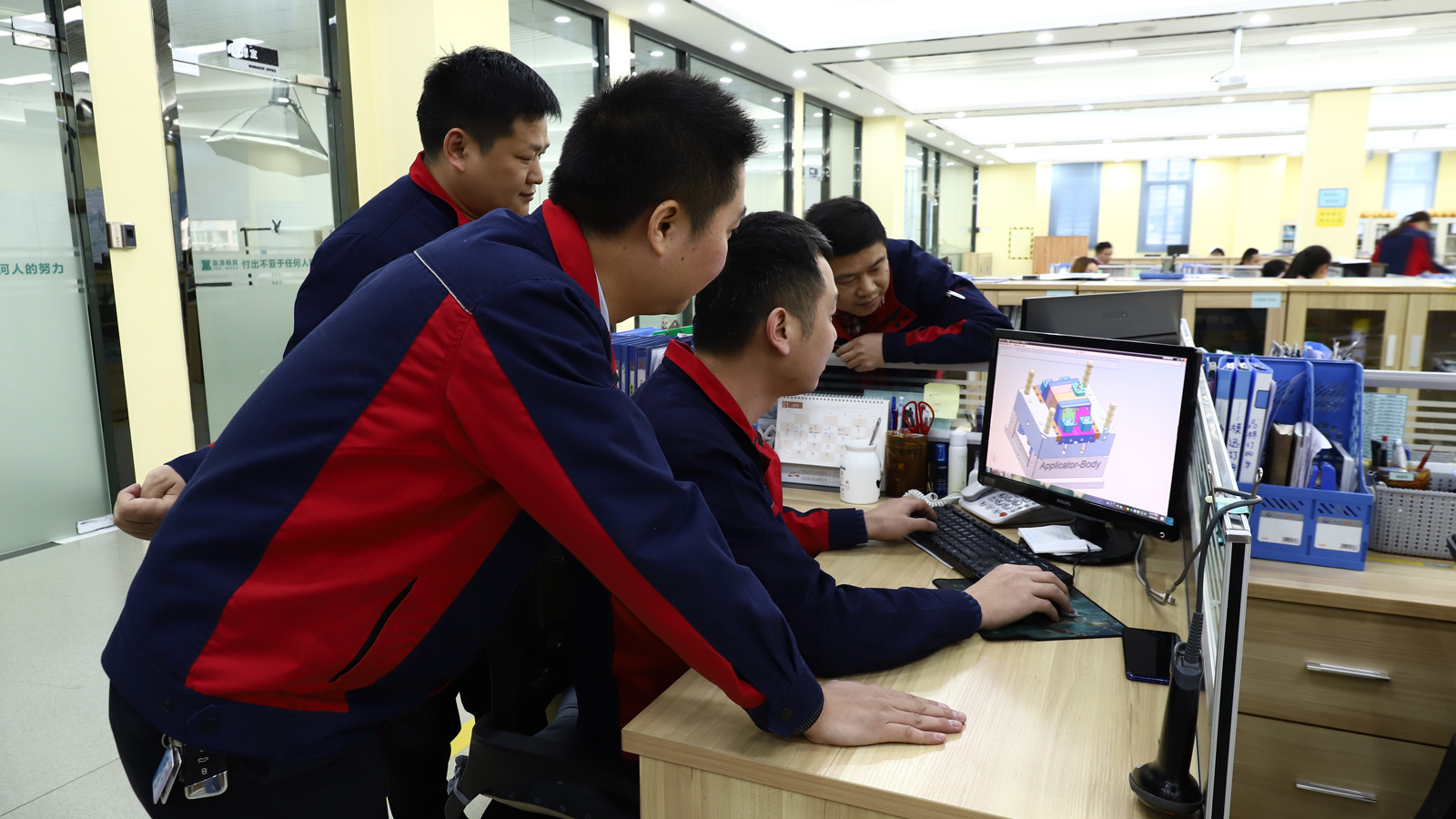
Plastic molds are customized products, with every set tailored to the specific requirements of clients. From the mold design proposal to the confirmation of various details, active participation and timely feedback from clients are essential. This is akin to a relay race. After the mold factory completes a stage of work, it passes the “baton” to the client for confirmation. Only when the client provides prompt feedback can the mold factory swiftly arrange the next steps. If the client’s feedback is slow, the mold factory can only wait, thereby prolonging the entire manufacturing cycle. For instance, in the design proposal confirmation stage, if the client has doubts about certain design details but fails to raise them promptly, and the mold factory proceeds with the original plan, subsequent modifications and rework are likely to be required. This not only wastes time but also increases costs.
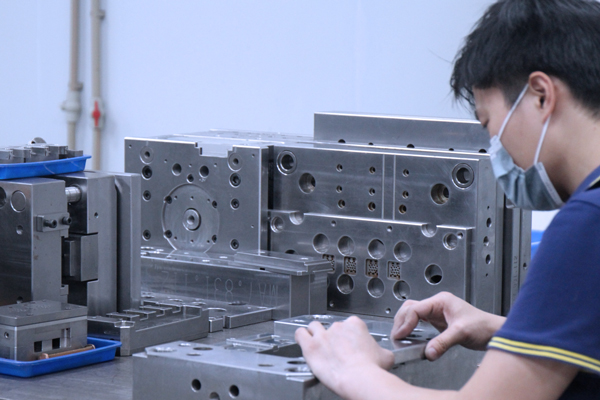
Manufacturing Process Difficulty: The “Obstacle” Challenging Production
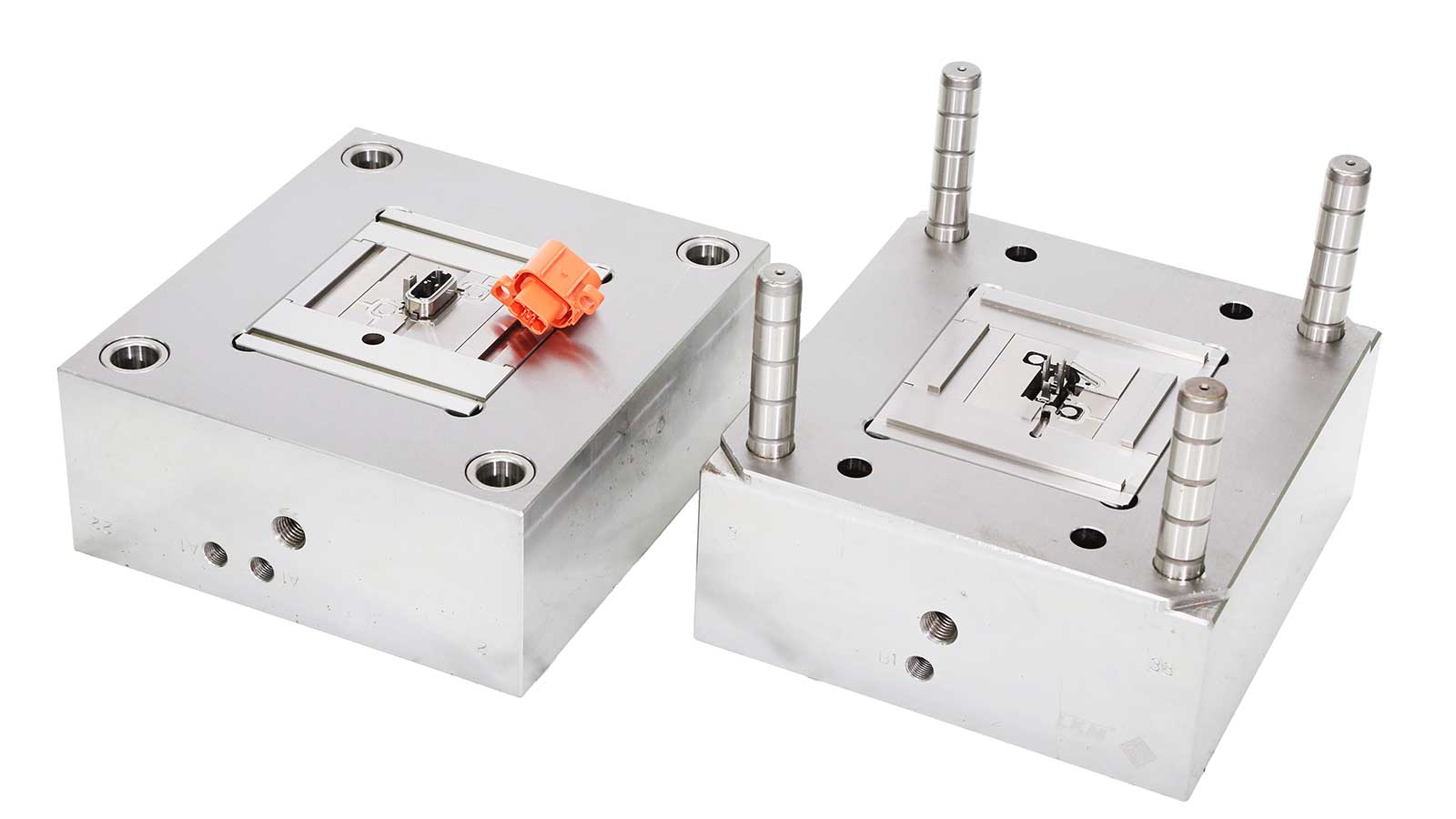
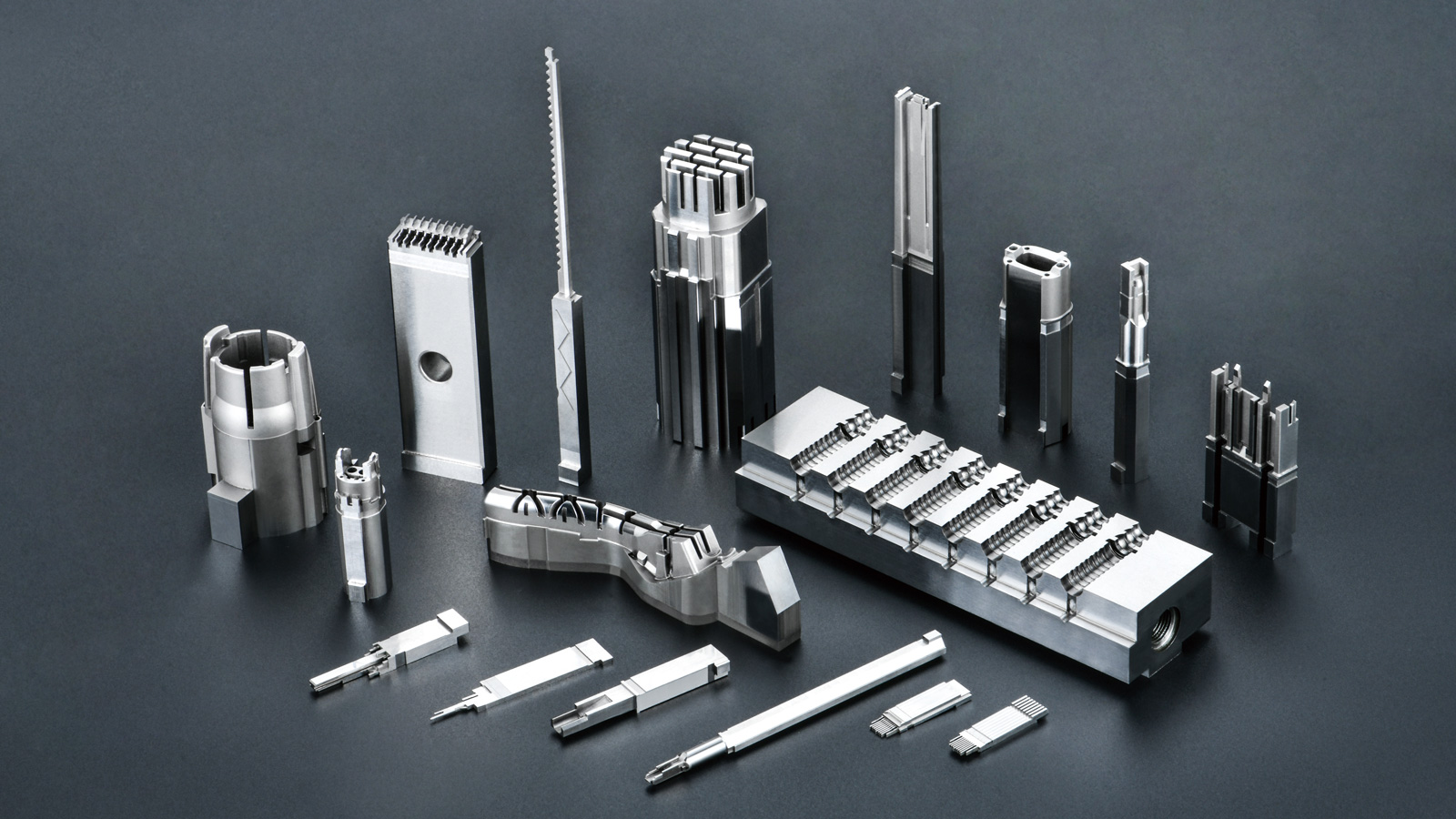
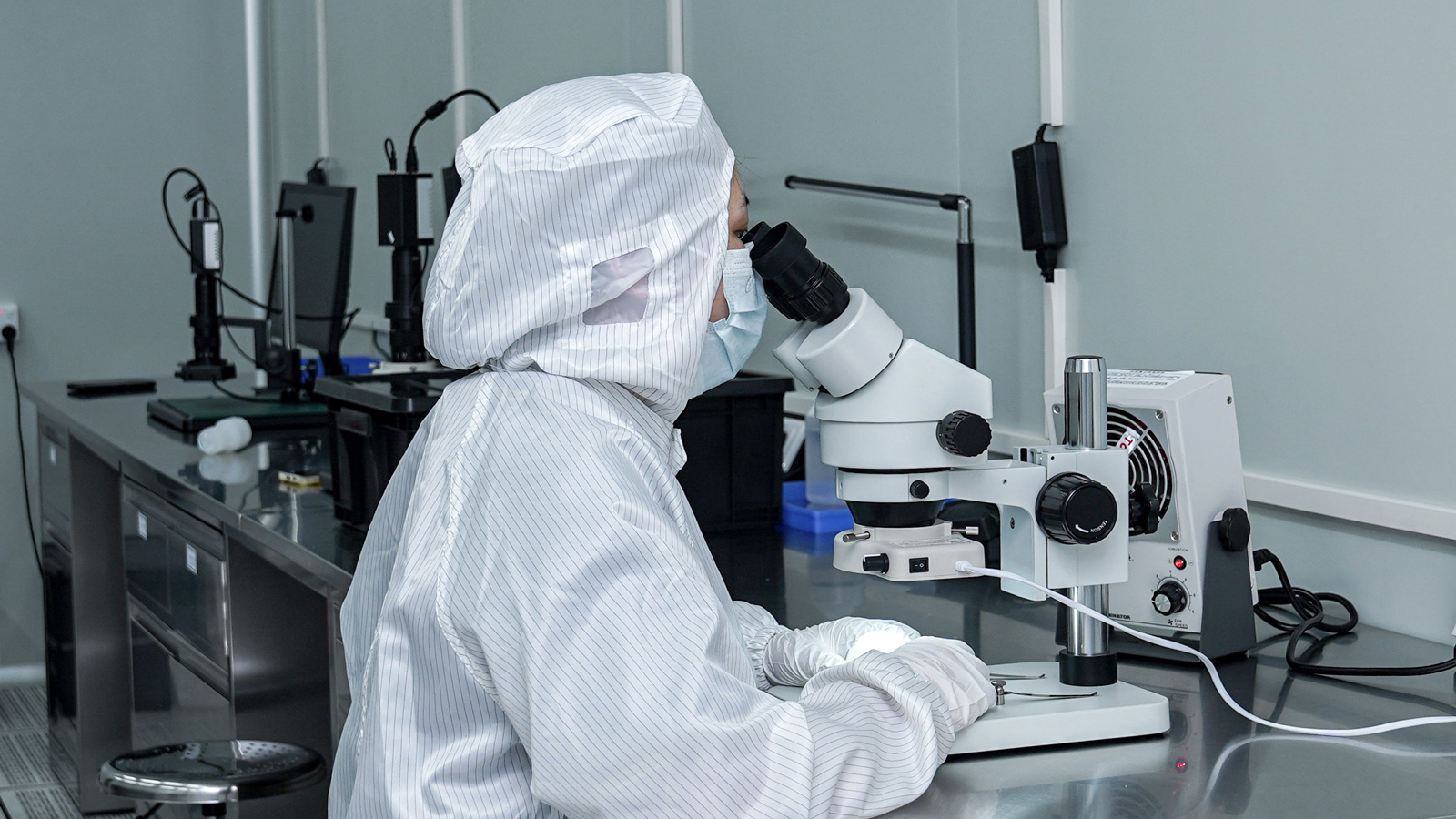
The manufacturing process difficulty is a significant factor influencing the delivery time of plastic molds, primarily depending on the production difficulty of the plastic part samples provided by clients. The more complex the shape of the plastic part, the higher the precision and structural requirements for the mold, and the greater the manufacturing difficulty. For example, some plastic parts with complex curved surfaces, tiny holes, or fine textures require more advanced processing equipment and techniques during mold manufacturing, such as high-speed milling and electrical discharge machining. Moreover, complex mold structures may necessitate multiple mold trials and adjustments to ensure that the produced plastic parts meet quality standards. Each mold trial consumes a certain amount of time, manpower, and material resources, so the greater the process difficulty, the longer the required time.
Projected Production Volume: The “Scale Variable” Affecting Molds
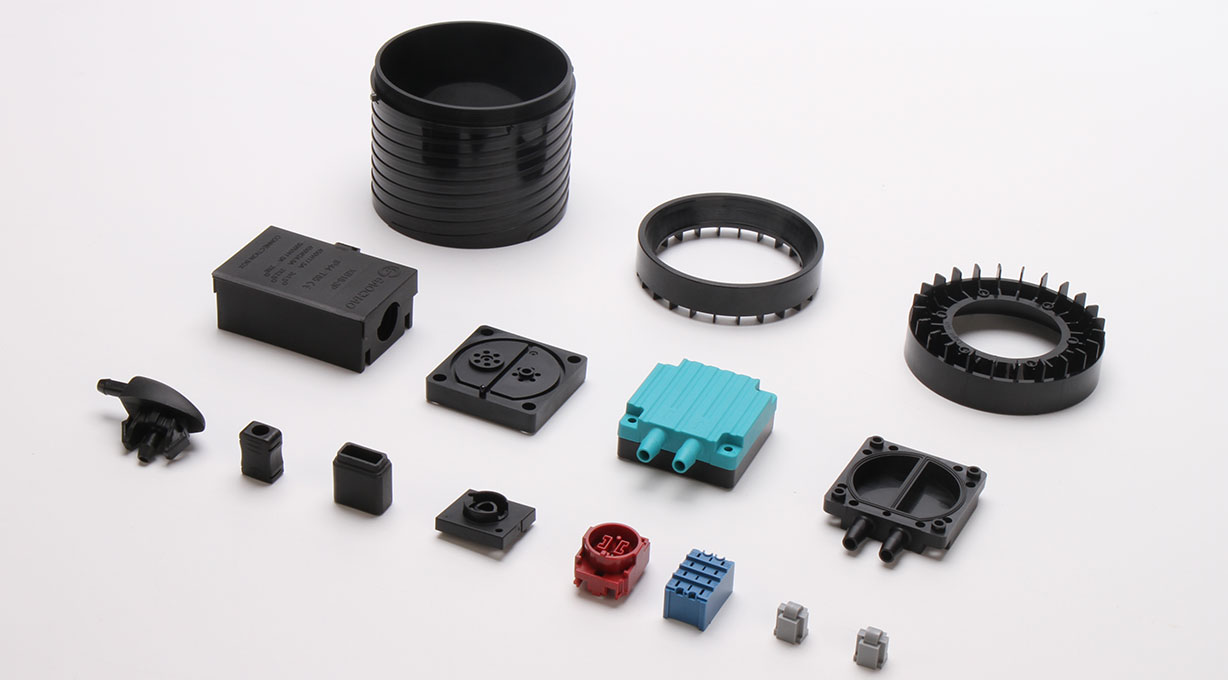
The client’s projected production volume is closely related to the number of cavities in the plastic mold, which in turn directly impacts the mold manufacturing time. If the client expects a large production volume, to meet the demands of mass production, the mold needs to be designed with more cavities. More cavities mean a more complex mold structure, increasing the manufacturing difficulty and time. Although the mold manufacturing time is extended, in subsequent production, multiple plastic parts can be molded at once, significantly improving production efficiency and reducing product costs. Conversely, if the client’s projected production volume is small, the number of mold cavities can be reduced, resulting in a shorter manufacturing time.
A combination of factors influences the manufacturing cycle of plastic molds. Mold factories must fully recognize these factors and implement effective project management and control measures to reasonably plan production and ensure the timely delivery of high-quality molds. For clients, understanding these factors also facilitates better communication and cooperation with mold factories, thereby promoting the smooth progress of projects.











